A Safety Mooring Rope is a critical factor that ensures the stability of fishing vessels and aquaculture platforms, helping minimize the risk of anchor drifting, rope failure, and equipment damage during rough sea conditions. Many boat operators focus only on vessel weight while overlooking material type, diameter, or abrasion resistance, which can lead to dangerous failures offshore. In this guide, SIAM Brothers Vietnam provides a comprehensive framework to help you select mooring ropes that meet industry standards and match specific sea conditions and applications. You will also learn how to inspect rope integrity, detect early signs of damage, and apply proper maintenance practices to extend service life. This is an essential resource for vessel owners seeking to improve safety and operational efficiency.
1. What Is a Safety Mooring Rope? Basic Standards and Technical Requirements
A Safety Mooring Rope is a specialized rope designed to maintain vessel and cage stability under varying environmental conditions. Selecting the correct mooring rope significantly reduces the risks of anchor drift, rope twisting, overload failure, or equipment damage, especially in rough coastal areas. To choose properly, you need to understand the following foundational technical factors.

Key Technical Standards of a Safety Mooring Rope
1.1 Breaking Load
- Indicates the maximum load the rope can withstand before failure.
- Plays a crucial role in ensuring consistent durability when the vessel experiences movement, shock loads, or current variation.
- Users should select a rope with a safety factor 4–6 times higher than the vessel’s operating weight or required holding load.
1.2 Elongation
- Rope elasticity helps absorb sudden shock loads caused by waves or abrupt vessel movement.
- Each material has a different elongation level, contributing to variations in safety and durability.
- In rough seas, adequate elongation helps prevent anchor-line breakage or fitting fractures.
1.3 Abrasion Resistance
- Mooring ropes often rub against boat edges, metal fittings, and cage structures, making abrasion a major cause of degradation.
- High abrasion resistance maintains breaking strength over long-term use.
- Users should inspect all contact points frequently to ensure continued safety.
1.4 UV and Marine Environment Resistance
- UV rays, saltwater, and temperature changes accelerate rope aging.
- A Safety Mooring Rope must resist UV exposure and moisture to perform reliably offshore.
- Materials such as PP, PE, and Polyester offer different levels of UV durability that directly influence service life.
1.5 Rope Construction and Fiber Density
- Tight, uniform construction minimizes twisting, fraying, or strand separation during high-friction operations.
- Consistent fiber density helps the rope maintain shape and load performance under sudden tension.
- Three-strand and eight-strand constructions are common choices for fishing vessels and aquaculture cages due to their stability and ease of handling.
2. Types of Safety Mooring Rope: PP, Nylon, Polyester, Composite – Practical Advantages and Limitations
2.1 Polypropylene (PP) Mooring Rope
Advantages
- Lightweight and easy to handle during mooring operations.
- Floats on water, reducing the risk of entanglement with propellers.
- Cost-effective and widely available, ideal for small vessels and medium-scale fish cages.
- Strong chemical resistance in brackish and marine environments.
Limitations
- Lower abrasion resistance; requires more frequent inspections.
- Medium elasticity, less suitable for high-wave areas.
- Shorter service life compared with Nylon and Polyester in long-term mooring.
2.2 Nylon Mooring Rope
Advantages
- High elasticity absorbs shock loads effectively, suitable for rough-sea operations.
- Excellent breaking strength and stability in demanding environments.
- Longer lifespan than PP due to superior abrasion resistance.
Limitations
- Absorbs water and becomes heavier over time.
- Higher cost than PP.
- Does not float; requires proper positioning to avoid propeller entanglement.

2.3 Polyester Mooring Rope
Advantages
- Strong, stable breaking strength with minimal stretch—ideal for fixed mooring of HDPE fish cage systems.
- Superior UV resistance, reducing aging under strong sunlight.
- Does not absorb water and maintains consistent weight during long-term immersion.
Limitations
- Low elasticity makes it unsuitable for areas requiring high shock absorption.
- Higher cost than PP and often comparable to or higher than Nylon.
2.4 Composite Mooring Rope
Advantages
- Combines the durability of synthetic fibers with the structural stability of composite materials.
- Excellent abrasion resistance and long-term stability, ideal for large-scale aquaculture mooring systems.
- Reliable performance under heavy load and deep-water conditions.
Limitations
- Higher initial investment.
- Requires manufacturing by specialized producers to ensure consistent material quality.
3. How to Choose the Right Safety Mooring Rope for Fishing Boats & Aquaculture Cages
3.1. Choosing Based on Vessel Capacity and Size
3.1.1. Vessels Under 50 HP
- Prioritize PP or Nylon Safety Mooring Rope with small to medium diameters for easier handling.
- Good elasticity helps reduce tension when anchoring nearshore or in areas with mild currents.
3.1.2. Vessels from 50–150 HP
- Choose Nylon or Polyester ropes to ensure higher load-bearing capacity.
- Pay attention to rope elongation to minimize shock load on anchor fittings in rough waves.
3.1.3. Large-Capacity Offshore Vessels
- Prefer Polyester or Composite Safety Mooring Rope for long-term durability.
- Combine with a steel chain at the rope’s front section to increase bottom grip and reduce abrasion.
3.2. Choosing Based on Water Conditions – Seawater, Brackish Water & Strong Currents
3.2.1. Rough Seas or Monsoon Regions
- Nylon is suitable due to its natural stretch, which absorbs shock loads when the vessel changes direction.
- Avoid using PP ropes in long-term rough-sea conditions.
3.2.2. Brackish Water or Areas with Many Obstacles
- Polyester is the optimal choice thanks to its UV resistance and high abrasion durability.
- A Safety Mooring Rope should have an outer protective layer or tight-braided construction to reduce fraying.

3.3. Choosing Based on Operational Needs & Usage Frequency
3.3.1. Boats Operating Daily
- Lightweight, easy-to-handle ropes such as PP or Nylon are appropriate.
- Perform regular inspections because frequent anchor deployment increases abrasion.
3.3.2. HDPE Fish Cage Systems
- Use Polyester or Composite ropes to ensure stable mooring performance over long periods.
- Combine with high-quality connectors and braided lines to prevent rope twisting.
4. Safety Mooring Rope Inspection Guide – 10-Step Checklist Before Sailing
4.1. Inspect Rope Condition and Connection Points
4.1.1. Inspect Rope Surface
- Look for signs of fuzzing, abrasion, fiber breakage, or unusual discoloration.
- Pay extra attention to areas in contact with boat edges, anchor fittings, or the seabed.
4.1.2. Inspect Knots and Hardware
- Ensure knots are not twisted, loose, or slipping.
- Check stainless-steel shackles, D-shackles, and safety clips for corrosion.
4.2. Assess Rope Strength and Load Capacity
4.2.1. Evaluate Elasticity by Rope Type
- Nylon: Check whether the rope still maintains proper stretch.
- Polyester & Composite: Look for signs of stiffness, hardening, or reduced structural stability.
4.2.2. Compare With the Vessel’s Actual Load
- Ensure the rope diameter and construction still meet pulling forces in high-wave areas.
- Replace the rope if abrasion exceeds 30% of the allowable threshold.
4.3. Evaluate Environmental Wear from Marine Exposure
4.3.1. UV Damage
- Inspect sections above the waterline, as these areas degrade the fastest.
- Replace the rope if it becomes dull, brittle, or shows UV-aging marks.
4.3.2. Saltwater & Current-Induced Abrasion
- Observe sections near the seabed or in fast-flowing water.
- A Safety Mooring Rope must maintain consistent strength throughout its entire length.

- Ensure the rope does not get pinched or stuck in the deck rollers or guide channels.
- Inspect pulleys, rollers, and fairleads for wear or rust.
- Check installation points such as cleats, eye plates, and crossbars.
- Inspect all attachment systems to avoid rope twisting or anchor-point failure.
4.5. The 10-Step Checklist for Safety Mooring Rope Inspection Before Departure
Step 1: Inspect the entire rope length from end to end.
Step 2: Check abrasion, fuzzing, and fiber damage.
Step 3: Inspect knots, connections, shackles, and safety pins.
Step 4: Evaluate rope elasticity according to rope type.
Step 5: Inspect sections frequently submerged or rubbing against rocks.
Step 6: Ensure the rope length matches the anchoring depth.
Step 7: Check chains, swivels, and all accessories.
Step 8: Perform a tension simulation to assess shock-load resistance.
Step 9: Record unusual signs for future monitoring.
Step 10: Replace the rope immediately if damage exceeds the safety limit.
5. How to Tie & Secure a Safety Mooring Rope – The 7 Essential Mooring Knots
5.1. Key Principles When Tying a Safety Mooring Rope
5.1.1. Ensure Proper Tension and Load Distribution
- Choose a tying point that distributes tension evenly across the rope to reduce localized abrasion.
- Avoid tying the rope directly onto sharp metal edges, which can cut fibers during mooring.
5.1.2. Maintain the Correct Rope Length Ratio
- Keep the rope length at 3 to 5 times the water depth.
- Avoid overstretching, as excessive tension increases shock loads in rough seas.
5.2. Seven Essential Knots for Safety Mooring Rope
5.2.1. Bowline Knot
- Creates a fixed, secure loop that does not tighten under heavy load.
- Suitable for attaching the Safety Mooring Rope to mooring rings, anchors, or stainless-steel shackles.
5.2.2. Anchor Hitch
- Provides excellent stability at the anchor point and prevents slipping in deep-water mooring.
- Ideal for fishing vessels operating in strong currents.
- Delivers high strength and strong holding capacity; suitable for Nylon or Polyester ropes.
- Minimizes twisting during continuous loading.
- Works as a stopper knot to prevent the rope from slipping through pulleys or fairleads.
- Commonly used in aquaculture mooring systems.
5.2.5. Double Sheet Bend
- Used for joining two ropes of different diameters.
- Useful when extending the Safety Mooring Rope for deep-water mooring.
5.2.6. Clove Hitch
- Ideal for fastening the rope to posts, rails, or mooring bollards.
- Easy to release when changing mooring points.
5.2.7. Rolling Hitch
- Allows the rope to grip firmly onto surfaces without slipping, even under wave shock.
- Useful for mooring near rocky areas or in turbulent currents.

6. FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions About Safety Mooring Rope
6.1. How long can a Safety Mooring Rope be used before replacement?
- Lifespan depends on material and operating environment.
- Nylon and Polyester ropes on fishing vessels typically last 12–24 months with proper inspection.
- Composite ropes may last longer if maintained correctly and not subjected to overload.
6.2. How do I choose the right rope diameter for a fishing boat or aquaculture system?
Select based on vessel size and mooring conditions:
- Small boats: 8–16 mm
- Medium boats: 18–24 mm
- Large vessels or fish cages: 24–36 mm
- Rope length should be 3–5 times the mooring depth for optimal load distribution.
6.3. Can PP rope be used in all mooring conditions?
- PP rope is lightweight and easy to handle but has low stretch and wears quickly in heavy waves.
- It suits small boats, calm waters, or temporary mooring—not recommended for long-term or rough-sea mooring.
6.4. How do I inspect a Safety Mooring Rope before departure?
- Follow the 10-step checklist: surface condition, splices, knots, elasticity, abrasion marks, discoloration, waterlogging, and sand contamination.
- Apply a light tension test to ensure remaining load capacity.
6.5. Do I need accessories with the Safety Mooring Rope?
- Yes. Stainless-steel shackles, anchors, swivels, and chains increase durability and safety.
- Especially for large vessels or aquaculture cages, accessories ensure even load distribution and reduce localized wear.
- Replace the rope if fibers are frayed, discolored, or hardened;
- if splices slip, knots fail to hold;
- or if the rope has been overloaded or exceeded its recommended lifespan.
6.7. How can I extend the lifespan of a Safety Mooring Rope?
- Store the rope away from direct sunlight, chemicals, and oil.
- Rinse thoroughly after use in seawater.
- Inspect regularly and remove the rope when not in use for long periods.
6.8. Where can I buy high-quality Safety Mooring Rope in Vietnam?
- SIAM Brothers Vietnam manufactures and supplies high-quality Safety Mooring Ropes for fishing vessels, HDPE aquaculture cages, and marine applications.
- Local production reduces shipping costs and ensures fast delivery nationwide.
- Purchase through the official website or authorized distributors to avoid counterfeit products.
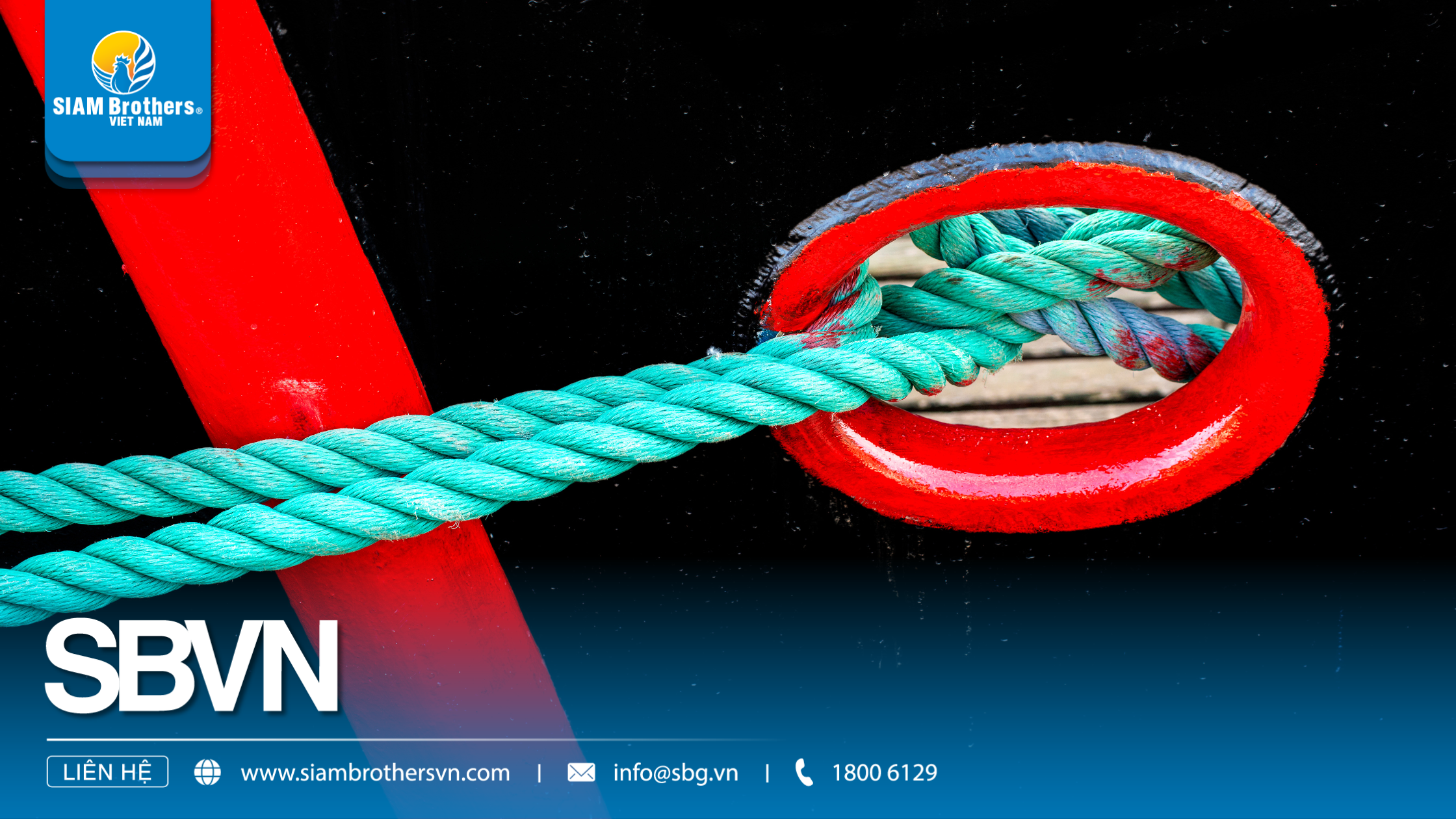
Safety Mooring Rope plays a crucial role in ensuring the stability and operational safety of fishing vessels and aquaculture systems. Choosing the right rope material, performing regular inspections, using proper knots, and maintaining the rope correctly all help extend its lifespan and reduce the risk of breakage. PP, Nylon, Polyester, and Composite ropes each offer distinct advantages when used according to recommended guidelines. Fishermen and cage operators should monitor signs of wear, follow inspection checklists, and replace ropes when necessary.
Choose a reliable, high-quality Safety Mooring Rope from trusted manufacturers like SIAM Brothers Vietnam to safeguard assets and enhance marine productivity. Contact us today!
Source: SIAM Brothers Vietnam
Contact us:
► Address: 5th floor, VRG Building, 177 Hai Ba Trung Street., Xuan Hoa Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
► Hotline: 1800 6129
► Tel: (+84) 28 38 912 889
► Email: info@sbg.vn
► Follow us for more details at: Facebook - Zalo OA - Tiktok - Youtube - LinkedIn
Download SBVN ID app here:
► CHPlay
► Appstore







